As of the writing of this article, America is in the midst of perhaps the most contentious and contested presidential election in recent history. The 2020 election between Donald Trump and Joe Biden remains undecided as vote counts continue and legal battles begin. Quickly earning a position among the elections of 1800, 1825, 1876, and 2000 as one for the books, this election’s big question surrounds the novel insertion of wide spread mail-in-ballots and the increased potential for voter fraud. Last minute changes in election laws set the stage for lengthy litigation concerning whether or not such alterations were constitutional, and widespread reports of errors, irregularities, and criminal activity has rocked many people’s faith in the legitimacy of the vote.

The unfortunate reality is that from the beginning of elections there have been people who attempted, and in many cases succeeded, at buying, cheating, and stealing their way into political office. America, for all her virtues, has been no different than other places throughout history. Wherever there is a system there are those who will seek to game it through illegitimate practices. As the Scriptures explain, and the Founding Fathers repeatedly affirmed throughout their writings, “the heart is deceitful above all things, and desperately wicked: who can know it?” (Jeremiah 17:9).
Even back in in the colonial period of American history, election fraud was such a problem that some of the earliest laws on the books were anti-fraud legislation attempting to ensure free and fair elections. Massachusetts had passed laws as early as 1643, and by the mid-1700s at Rhode Island, New Jersey, Virginia, and other colonies had followed suit.[i] However, wherever there are rules there will be people to break them, and some early American elections were decided based on which candidate provided more “incentives,” whether it be financial or otherwise.[ii] During the Revolutionary War and shortly thereafter, the Founders attempted to secure elections by establishing many state level injunctions against illegal voting practices. The 1776 Pennsylvania constitution, for example, explicitly punished bribery while North Carolina passed anti-fraud laws in 1777.[iii] By 1784 New Hampshire barred anyone convicted of fraud ineligible for holding office.[iv]
After the ratification of the Constitution, voter fraud continued in both tried and true ways as well as new various methods. In 1816, a printed letter warns voters of “spurious and captive tickets and circulars” which struck the Federal Republican candidate for Senate off of the ticket and replacing him with the Democrat running for office.[v] The deception was discovered the day before the election and the Republican letter bemoans that “it is the object of a few who would sacrifice their party for their private interest.”[vi]
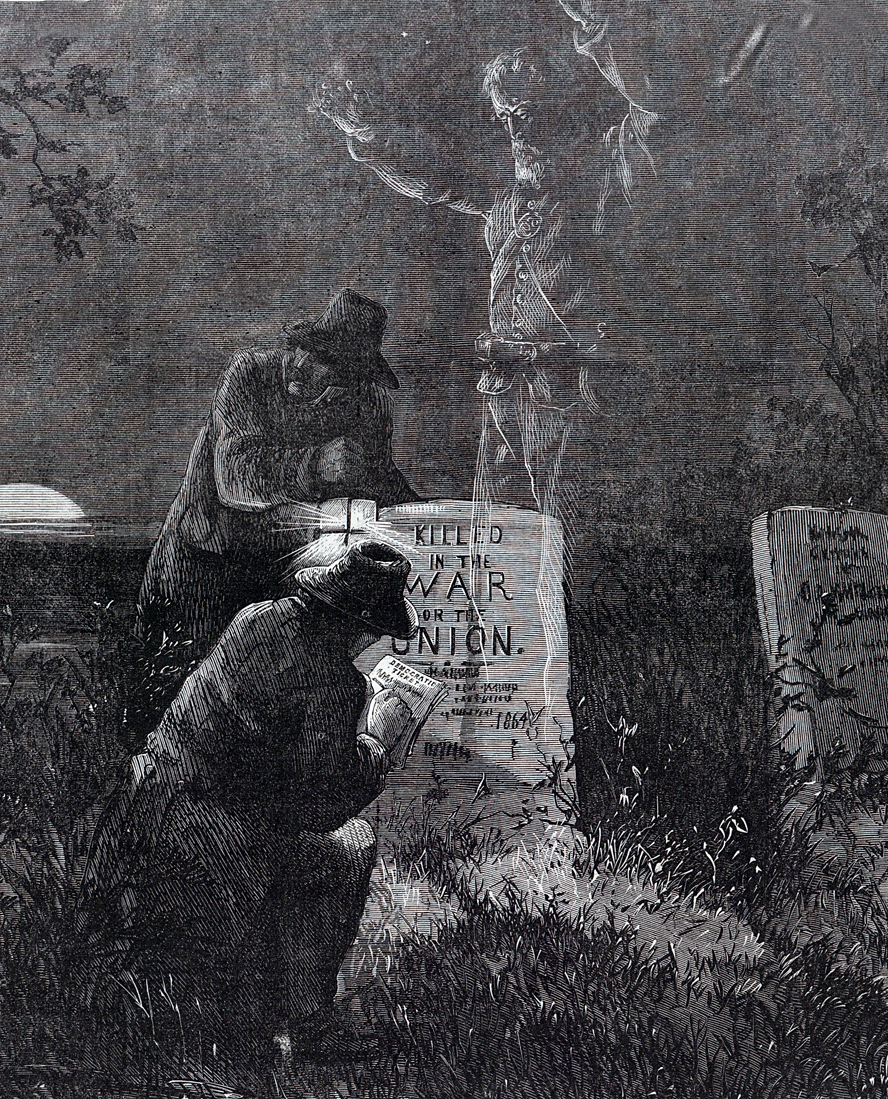

During the contentious years of the Civil War, when brother killed brother, the evils of voter fraud paled in comparison to the greater wickedness afflicting the nation. Those who were content to hold their fellow man in slavery could not be bothered by the lesser immorality of illegal voting. The 1864 election cycle witnessed fraud which parallels the modern-day issues in a surprisingly close manner. Pro-slavery Northern Democrats—nicknamed Copperheads after the venomous snake—went to great lengths attempting to unseat Abraham Lincoln. Harpers Weekly, one of the major newspapers of the day, highlighted how the Copperheads would use the names of recently deceased soldiers to vote illegally.[vii]
On top of that, the Copperheads also schemed to use the mail-in-ballots sent out to the troops as a way of illegally siphoning votes away from Lincoln. After a sting operation revealed that the pro-slavery Democrats had been forging the signatures of soldiers on blank ballots the plot was uncovered and the perpetrators thrown in prison. Despite the seriousness of the voter corruption, the Copperhead agents nevertheless joked saying, “dead or alive they would all had cast a good vote.”[viii]
After the Civil War and the enfranchisement of African Americans, Southern Democrats continued to engage in illegal voting activity such as ballot manipulation and intimidation. The end of Reconstruction as a political compromise following the contested 1876 presidential election opened the door for unchecked voter fraud and illegal election interference throughout southern states. Groups like the KKK (Ku Klux Klan) and the racist Democrats who started that group erected barriers and obstacles to prevent voting rights and transparency.[ix] Complicit in these schemes was an activist Supreme Court which in 1883 struck down all the civil rights passed by the Republican Congress during and in the years following the Civil War.[x]
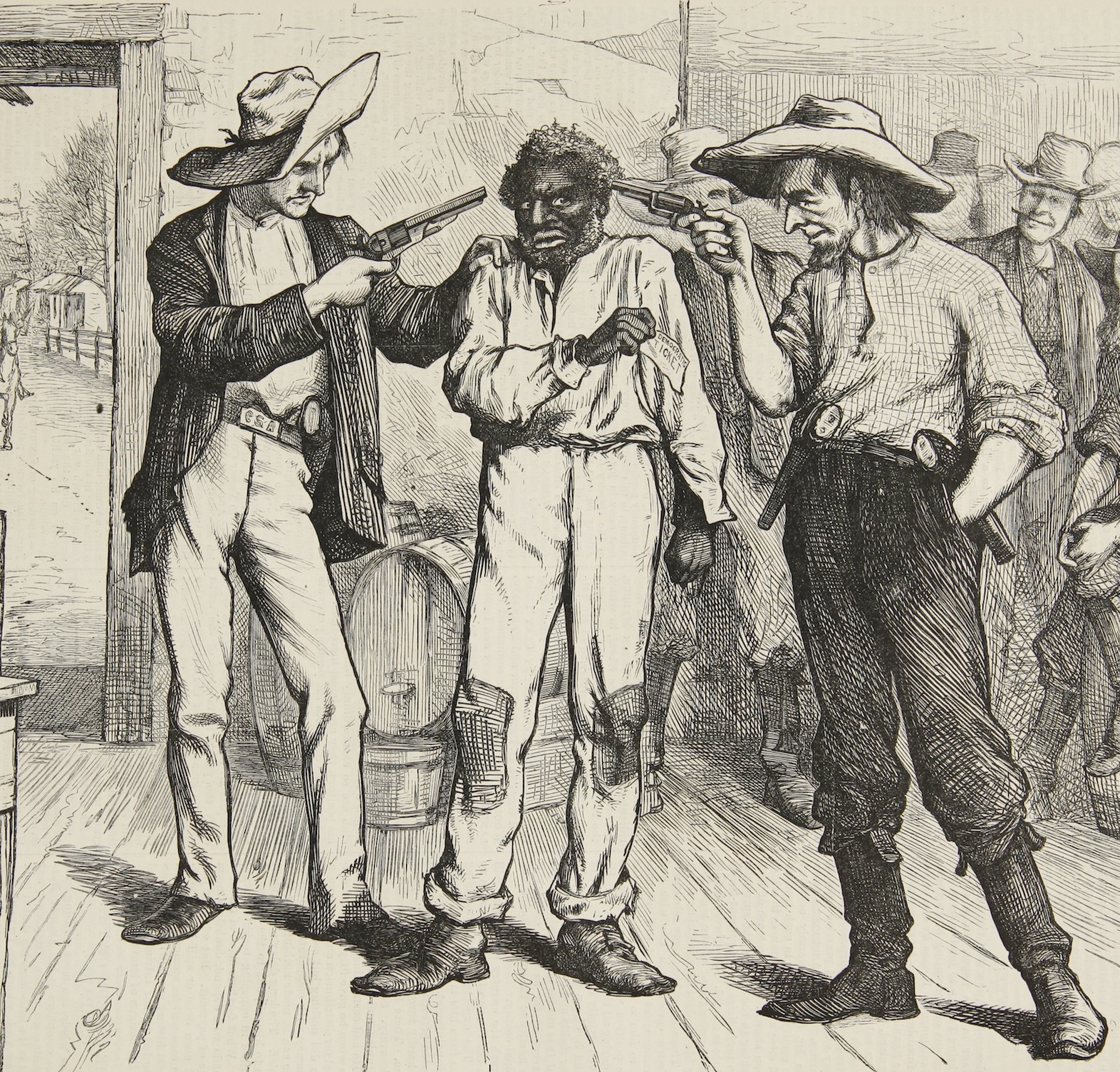

With the pathway cleared for Jim Crow, poll taxes, voter intimidation, and ballot-box stuffing, the Southern political machines ensured that no one supporting racial equality would be elected under their watch. The influential Harpers Weekly once again stepped in to illustrate the coercive tactics with the political cartoon pictured which was titled “Of Course He Wants to Vote the Democrat Ticket.”[xi]
While such illegitimate elections continued apace in the South, by the early 1900s voter fraud was pervasive in rural counties with people selling their votes and politicians more than willing to buy them. For instance, in poverty-stricken Adams County, Ohio, in 1911 a judge convicted some 1,700 people for selling their votes to the highest political bidder—nearly 25% of total electorate.[xii] One of the citizens confessed to the judge, “I know it isn’t right, but this has been going on for so long that we no longer looked upon it as a crime.”[xiii] It was just the way things were.
A review of American elections in 1918 explained that during the late 19th and early 20th century, “the most common electoral fraud is bribery,” but said further that the “false counting of ballots has been an easy and common way to vitiate [invalidate] election results.”[xiv] After the rampant and unchecked fraud of the late 1800s there was a, “gradual awakening of the American people to corrupt conditions existing in their government,” and the widespread “defilement of the ballot-box.”[xv]
This certainly led to attempts to pass laws preventing politicians from stealing elections, but how can one expect the people who cheated their way into office to stop themselves from doing it again? Therefore, although certainly legislation was passed, by-in-large the political bosses continued to buy, sell, and trade elections. A notorious example happened in 1932 when long-time political boss, Senator Huey “Kingfish” Long of Louisiana, was exposed rigging votes which led to the indictment of 513 election officials in New Orleans.[xvi]

More famously, in 1948 future president Lyndon Baines Johnson beat out his opponent in the Democrat Party primary for Senate by just 87 votes out of a total 988,295. Where did these votes come from? A specific voting location called “Ballot Box 13” which just so happened to show up and have just the number of votes he needed.[xvii] Although rumors and winks circulated for decades concerning Johnson’s unique method of “campaigning,” the suspicions were confirmed in 1977 when one of Johnson’s operatives confessed to stuffing the votes himself. “Johnson didn’t win that day. We stole it for him.”[xviii]
But certainly, this doesn’t happen today, does it? While technology has changed, regrettably human nature and fallibility hasn’t. Over the past few decades there have been many instances of clearly documented illegal activity surrounding elections—and often the technology has only made it easier than ever to rig an election.
For example, during the transition from paper ballot to electronic machines in the late 1990s and early 2000s, the number of last minute “glitches” which changed the course of an election are astonishing. The machines used by Election Systems and Software (ES&S)—one of the largest voting machine companies—stole governors’ races, flipped ballot initiatives, and caused thousands of votes to be left on the cutting room floor. Investigative journalists identified no less that fifty-six instances of these miraculous glitches occurring wherever these machines were.[xix]
Nebraska’s 1996 race for Senate witnessed the Republican candidate, Chuck Hagel, beat the Democrat governor who had led in the polls throughout the race by fifteen points.[xx] This was the first time in decades that Nebraska had sent a Republican senator to Congress. It was an upset for the ages. Who was this up-and-coming political star? Well, up until fourteen days before announcing his run for office Hagel had been the CEO of ES&S—the company whose machines would be the ones tallying the votes. And later, he managed to mask and hide his continued ownership of substantial investments in the company.[xxi] When rumors of a presidential run floated around Hagel, his old company was responsible for counting some 56% of the nation’s vote.[xxii] Unfortunately any opportunity to concretely verify fraud have long since passed as all investigations and complaints to the Senate Ethics Committee were squashed before getting off the ground.

Election Systems and Software has had to reshuffled the deck and sell off certain parts of the business, some of which were siphoned off into a new company called Dominion—but the danger remains the same. In fact, as of 2017, together ES&S and Dominion control some 81% of the national voting machines which were responsible for counting the ballots of 154,387,532 registered voters.[xxiii] Dominion has continued to expand its influence in American elections and replaced all of Georgia’s voting systems immediately prior to the 2020 presidential cycle.[xxiv]
On top of the red flags surrounding the machines themselves, comprehensive studies of the voter rolls in the 2016 and 2018 election cycles revealed troubling data which made the stage ripe for fraud. Heading into the 2020 election cycle there were 349,773 dead people on voter rolls across the country, with over half of them being in New York, Texas, Michigan, Florida, and California.[xxv] In 2016 and 2018 there were over 14,000 proven cases of voting after death, with North Carolina leading the nation by a 4-to-1 ratio.[xxvi] Such practices still continue, and just weeks before Election Day 2020, a man was arrested in Pennsylvania for applying for a mail-in-ballot for his dead mother.[xxvii]
Audits of the previous two elections revealed at least 81,649 cases of people voting twice—something completely illegal.[xxviii] Many of these cases hinged upon the easy accessibility to unsolicited mail-in-ballots—as was the case when a Democrat mayoral candidate in Texas was arrested on 25 counts of illegally possessing ballots and 84 counts of falsifying voter applications.[xxix] Likewise, 35,000 registrant files list commercial addresses instead of residential ones—an action which led Congressman Steve Watkins (R-Kansas) to face three felony counts of potential fraud in 2020.[xxx]
Between the vulnerability of voting machines and the rancid condition of voter registration rolls, the stage is set for widespread, nearly untraceable, and possibly irreversible fraud. Whether paper or electronic, Americans are susceptible to having their elections stolen from under their noses. Even in the months prior to the presidential election in 2020, arrests and criminal convictions have happened for illegal voting activities such as the fraudulent use of absentee ballots, duplicate voting, false registrations, ballot petition fraud, and illegal “assistance” at the polls.[xxxi]
In fact, just days before the election the Democrat presidential nominee Joe Biden declared in a press conference, while seemingly reading off a script, “we have put together, I think the most extensive and inclusive voter fraud organization in the history of American politics.”[xxxii]
Many people simply laughed at such a statement. In recent years, Biden has become infamous for incoherent statements and botching speeches even while using a teleprompter. Compilations of his gaffes from just the campaign trail alone easily extend upwards of a half an hour. But now that the election has been rife with hundreds of clearly suspicious cases of “glitches” and “irregularities,” perhaps Biden was just being honest. Rather than being yet another gaffe, perhaps it was a kind of “fraud-ian” slip.

Perhaps the most surprising facet of the 2020 election, however, has been the utter denial of even the possibility of voter fraud by legacy media conglomerates. These alleged investigative journalists turn a blind eye to both present evidence and historical fact when they collectively denounce “the myth of voter fraud.”[xxxiii] In fact, the same mass of media outlets which spent three years hopelessly searching for international election interference in the 2016 American election, scoff at even the mention of possible domestic election interference in 2020.
Historically, voter fraud has happened in America since its inception. That the mainstream media agencies refuse to acknowledge its existence does not alter the reality. Instead, such denial only makes them tacit accomplices in the death of the Republic. The same people who warn that democracy dies in darkness are the ones turning off the lights.
To entirely ignore or deny the existence of fraud is irresponsible, ignorant, or maliciously intentional. Everyone, no matter their political affiliation, should have an unquenchable desire for a transparent and airtight election process. Each fraudulent ballot discards someone’s legitimate vote. Every fake declaration silences someone’s real voice. Counterfeit elections devalue and debase the freedom and liberty of all Americans, ensuring nothing except the arbitrary control that the political elite may exert upon the people.
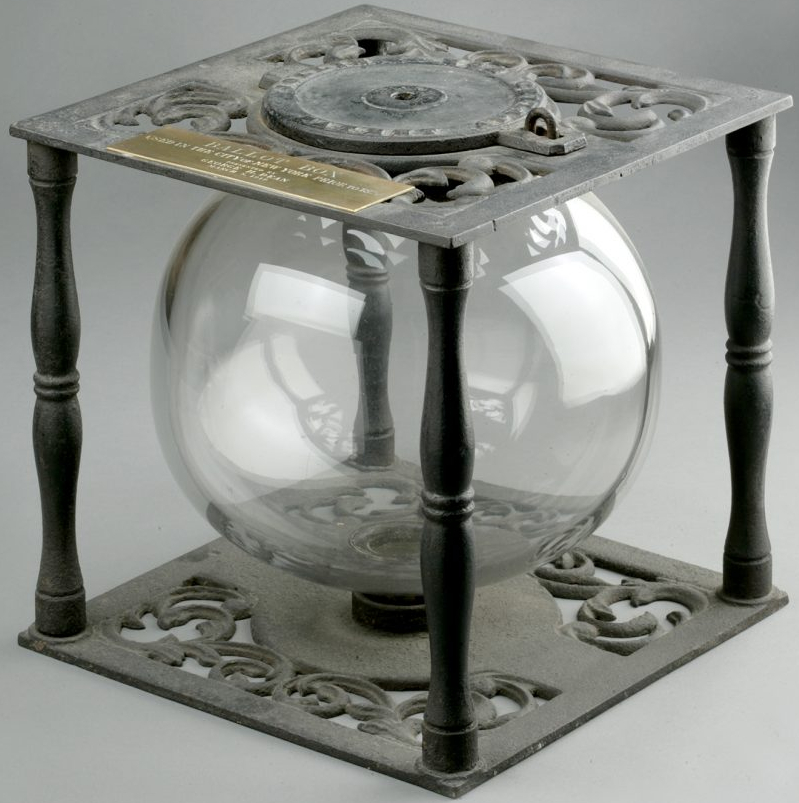

In the past, America turned began using glass ballot boxes (as pictured) which allowed people to see that no one was stealing the election.[xxxiv] It made the officials directly accountable to the people who were free to watch and observe their actions with full transparency. Over the years, the glass ballot box became a symbol of American freedom. A symbol now long forgotten—but one that needs to be resurrected. This is the true Cradle of Liberty—where the people are free to make their own decision, without coercion, fraud, or oppression, about who will represent them. Integrity is necessary for liberty, and the ballot boxes and voting processes of today ought to be just as transparent as the glass ones from yesteryear.
Endnotes
[i] The Encyclopedia Americana, s.v. “Electoral Fraud and Safeguards Against,” (New York: The Encyclopedia Americana Corporation, 1918), 10.70.
[ii] Tracy Campbell, Deliver the Vote: A History of Election Fraud, An American Political Tradition—1742-2004 (New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers, 2005), 5-7.
[iii] Tracy Campbell, Deliver the Vote: A History of Election Fraud, An American Political Tradition—1742-2004 (New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers, 2005), 9.
[iv] Tracy Campbell, Deliver the Vote: A History of Election Fraud, An American Political Tradition—1742-2004 (New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers, 2005), 9.
[v] “Election. Federal Republicans Beware!” 1816. Vote: The Machinery of Democracy (accessed November 8, 2020): https://americanhistory.si.edu/vote/paperballots.html.
[vi] “Election. Federal Republicans Beware!” 1816. Vote: The Machinery of Democracy (accessed November 8, 2020): https://americanhistory.si.edu/vote/paperballots.html.
[vii] “‘How the Copperheads Obtain their Votes,’ Thomas Nast, Harper’s Weekly, November 12, 1864, detail,” House Divided: The Civil War Research Engine at Dickinson College (accessed November 7, 2020): http://hd.housedivided.dickinson.edu/node/43183.
[viii] Josiah Benton, Voting in the Field: A Forgotten Chapter in the Civil War (Boston: Privately Printed, 1915), 164; see also, Donald Inbody, The Soldier Vote: War, Politics, and the Ballot in America (New York: Palgrave McMillian, 2016), 42.
[ix] See, for example, William Simmons, Men of Mark: Eminent, Progressive, and Rising (Cleveland: Geo. M. Rewell & Co., 1887), 348.
[x] Valeria Weaver, “The Failure of Civil Rights 1875-1883 and Its Repercussions,” The Journal of Negro History 54, no. 4 (1969): 369-370.
[xi] “‘Of Course He Wants to Vote the Democratic Ticket.’ A. B. Frost. From Harper’s Weekly, October 21, 1876,” The Newberry Digital Collections for the Classroom (accessed November 7, 2020): https://dcc.newberry.org/items/of-course-he-wants-to-vote-the-democratic-ticket.
[xii] Genevieve Gist, “Progressive Reform in a Rural Community: The Adams County Vote-Fraud Case,” The Mississippi Valley Historical Review 48, no. 1 (1961): 65.
[xiii] Genevieve Gist, “Progressive Reform in a Rural Community: The Adams County Vote-Fraud Case,” The Mississippi Valley Historical Review 48, no. 1 (1961): 71.
[xiv] The Encyclopedia Americana, s.v. “Electoral Fraud and Safeguards Against,” (New York: The Encyclopedia Americana Corporation, 1918), 10.70.
[xv] Robert Brooks, Corruption in American Politics and Life (New York: Dodd, Mead and Company, 1910), 206.
[xvi] Victoria Collier, “How to Rig an Election,” Harper’s Magazine (November 2012), accessed November 8, 2020: https://harpers.org/archive/2012/11/how-to-rig-an-election/.
[xvii] See, John Fund, Stealing Elections: How Voter Fraud Threatens Our Democracy (New York: Encounter Books, 2008), 12, 176-177; Robert Caro, The Years of Lyndon Johnson: Master of the Senate (New York: Random House Inc., 2009), 115-116.
[xviii] John Fund, Stealing Elections: How Voter Fraud Threatens Our Democracy (New York: Encounter Books, 2008), 177.
[xix] Bev Harris, Black Box Voting: Ballot Tampering in the 21st Century (Renton, WA: Talion Publishing, 2004), 4. Here.
[xx] Victoria Collier, “How to Rig an Election,” Harper’s Magazine (November 2012), accessed November 8, 2020: https://harpers.org/archive/2012/11/how-to-rig-an-election/.
[xxi] Bev Harris, Black Box Voting: Ballot Tampering in the 21st Century (Renton, WA: Talion Publishing, 2004), 27, 31. Here.
[xxii] Bev Harris, Black Box Voting: Ballot Tampering in the 21st Century (Renton, WA: Talion Publishing, 2004), 32. Here.
[xxiii] Lorin Hitt, The Business of Voting: Market Structure and Innovation in the Election Technology Industry (Philadelphia: Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, 2017), 14, 54. Here.
[xxiv] Dave Williams, “Georgia Chooses Denver Company to Install New Statewide Voting System,” Atlanta Business Chronicle (July 29, 2019), accessed November 8, 2020: https://www.bizjournals.com/atlanta/news/2019/07/29/georgia-chooses-denver-company-to-install-new.html.
[xxv] Critical Condition: American Voter Rolls Filled With Errors, Dead Voters, and Duplicate Registrations (Public Interest Legal Foundation, September 2020), 8.
[xxvi] Critical Condition: American Voter Rolls Filled With Errors, Dead Voters, and Duplicate Registrations (Public Interest Legal Foundation, September 2020), 8.
[xxvii] Carolyn Blackburn, “Man Arrested for Voter Fraud in Luzerne County,” WNEP News Station (October 21, 2020), accessed November 8, 2020: https://www.wnep.com/article/news/local/luzerne-county/man-arrested-for-voter-fraud-in-luzerne-county/523-7fc4fd2f-9105-47e7-a510-2b5ff176ab2c.
[xxviii] Critical Condition: American Voter Rolls Filled With Errors, Dead Voters, and Duplicate Registrations (Public Interest Legal Foundation, September 2020), 8.
[xxix] Matthew Impelli, “Texas Dem Mayoral Candidate Charged With Voter Fraud After Allegedly Applying for 84 Mail-in-Ballots,” Newsweek (October 13, 2020), accessed November 10, 2020: https://www.newsweek.com/texas-dem-mayoral-candidate-charged-voter-fraud-after-allegedly-applying-84-mail-ballots-1538644; Alex Samuels, “Carrollton Mayoral Candidate Arrested on Suspicion of Fraudulently Obtaining Mail-in-Ballots,” The Texas Tribune (October 8, 2020), accessed November 8, 2020: https://www.texastribune.org/2020/10/08/voting-fraud-arrest-carrollton/.
[xxx] Critical Condition: American Voter Rolls Filled With Errors, Dead Voters, and Duplicate Registrations (Public Interest Legal Foundation, September 2020), 30; Brian Lowry, “‘I Wasn’t Hiding the Ball.’ Watkins Admits Voting at Wrong Address, but Denies Intent,” The Kansas City Star (July 28, 2020), accessed November 8, 2020: https://www.kansascity.com/news/politics-government/article244541302.html.
[xxxi] See database, “Election Fraud Cases,” The Heritage Foundation (accessed November 7, 2020), https://www.heritage.org/voterfraud/search?combine=&state=All&year=2020&case_type=All&fraud_type=All; see also, Erin Anderson, “Texas Social Worker Charged With 134 Election Fraud Felonies,” Texas Scorecard (November 6, 2020), accessed November 8, 2020: https://texasscorecard.com/state/texas-social-worker-charged-with-134-election-fraud-felonies/.
[xxxii] Joseph Curl, “Biden Stumbles Through Final Days of Presidential Campaign,” The Daily Wire (November 2, 2020), accessed November 10, 2020: https://www.dailywire.com/news/biden-stumbles-way-through-final-days-of-presidential-campaign.
[xxxiii] E.g., Vera Bergengruen, “How Republicans are Selling the Myth of Rampant Voter Fraud,” Time (October 22, 2020), accessed November 7, 2020: https://time.com/5902728/voter-fraud-2020-2/; William T. Adler, “Why Widespread Voter Fraud is a Myth,” Center for Democracy & Technology (October 28, 2020), accessed November 7, 2020, https://cdt.org/insights/why-widespread-mail-in-voter-fraud-is-a-myth/; Amber McReynolds, “Let’s put the vote-by-mail “fraud” myth to rest,” The Hill (April 28, 2020), accessed November 7, 2020: https://thehill.com/opinion/campaign/494189-lets-put-the-vote-by-mail-fraud-myth-to-rest.
[xxxiv] Jennifer Nalewicki, “A Glass Ballot Box Was the Answer to Voter Fraud in the 19th Century,” Smithsonian Magazine (November 2, 2020), accessed November 10, 2020: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smithsonian-institution/glass-ballot-box-was-answer-voter-fraud-19th-century-180976171/.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
More Resources
Know the Truth and Protect Your Freedoms.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
Stay Informed with the Latest Resources
Enter your email address to receive our regular newsletter, with important information and updates right in your inbox!