Overview
Significantly, 1 Timothy 1:5 declares that the goal of the entirety of everything taught in the Scriptures is threefold:
The goal of our instruction is love from a pure heart, and a good conscience, and a sincere faith.
Significantly, the three are inseparable, and without a good conscience, there will not be either a sincere faith or a pure heart. It is therefore not surprising that developing, maintaining, and living according to a good conscience is referenced more than thirty times in the New Testament (cf. Acts 24:16, 1 Timothy 1:19, 3:9, 1 Peter 3:16, 21, Romans 13:5, 2 Corinthians 4:2, etc.).
In fact, 1 Corinthians 8:4-12 flatly states that if a Christian views something as a matter of conscience – if the inner voice that God has placed within him or her tells them that something is sin to them – they are not to violate their conscience; and if anyone makes them do so, then they “sin against Christ.” (This message is repeated in Romans 1:1-23, 1 Corinthians 10:28-32, and elsewhere.) Few subjects in the Bible are stressed as strongly as that of maintaining a pure conscience – of preserving the conviction that one will answer directly to God for what his religious faith requires him to do, or refrain from doing.
Strikingly, only nations who respect Biblical teachings and traditions offer protection for the rights of religious conscience. Secular and non-Biblical nations, and those with state-established churches (such as those that predominated in England and Europe at the time of the American Founding), do not allow rights of conscience but instead demand conformity, which often requires governmental punishment coercion concerning religious beliefs, which violates the Scriptures.
Christ Himself established religious non-coercion as the standard. His approach was so voluntary that He even directed His disciples that when they presented the Gospel to others, if someone was interested, then they could stay and share the message with them; but if someone did not want to hear, then they were to leave the area and not force the issue (Luke 10:8-12). There was absolutely no coercion. It was also this way with Paul and the other Apostles: in every case; hearers then chose whether or not to follow Christianity; there was never any penalty, pressure, or force levied against them.
As John Quincy Adams noted, Jesus Christ “came to teach and not to compel. His law was a Law of Liberty. He left the human mind and human action free.”1 Two generations later, legal writer Stephen Cowell (1800-1872) similarly avowed:
Nonconformity, dissent, free inquiry, individual conviction, mental independence, are forever consecrated by the religion of the New Testament as the breath of its own life – the conditions of its own existence on the earth. The book is a direct transfer of human allegiance in things spiritual from the civil and ecclesiastical powers to the judgment and conscience of the individual.2
And several generations after that, President Franklin D. Roosevelt continued to affirm the same truth, noting: “We want to do it the voluntary way – and most human beings in all the world want to do it the voluntary way. We do not want to have the way imposed. . . . That would not follow in the footsteps of Christ.”3
From the beginning, America faithfully observed these principles, refusing to apply government coercion or conformity to the religious beliefs and practices of individuals. But today, this is dramatically and rapidly changing, with government routinely requiring people of faith to violate their religious conscience, particularly on social issues such as those surrounding aspects of sexuality, whether the taking of unborn human life, contraception, or requiring participation in homosexual nuptials, affirmation of transgenderism, and other major sexual elements of the LGBT agenda.
The American Experience on Religious Conscience
Colonial Era
Many of the early colonists who came to America were familiar with the Bible teachings on conscience and brought them to America, where they took root and grew to maturity at a rapid rate, having been planted in virgin soil completely uncontaminated by the religious apostasy and routine violations of the rights of conscience that had characterized the previous millennia. Hence, Christianity as practiced in America became the world’s single greatest historical force in securing non-coercion, religious toleration, and the rights of conscience.
For example, in 1640, the Rev. Roger Williams established Providence (the city that became the center of the Rhode Island colony), declaring:
We agree, as formerly hath been the liberties of the town, so still, to hold forth liberty of conscience.4
Similar language and protections were also included in subsequent American documents, including the 1649 Maryland “Toleration Act,”5 the 1663 charter for Rhode Island,6 the 1664 Charter for Jersey,7 the 1665 Charter for Carolina,8 the 1669 Constitutions of Carolina,9 the 1676 charter for West Jersey,10 the 1701 charter for Delaware,11 the 1682 frame of government for Pennsylvania,12 and many others. As John Quincy Adams affirmed, “The transcendent and overruling principle of the first settlers of New England was conscience.”13
Revolutionary Era
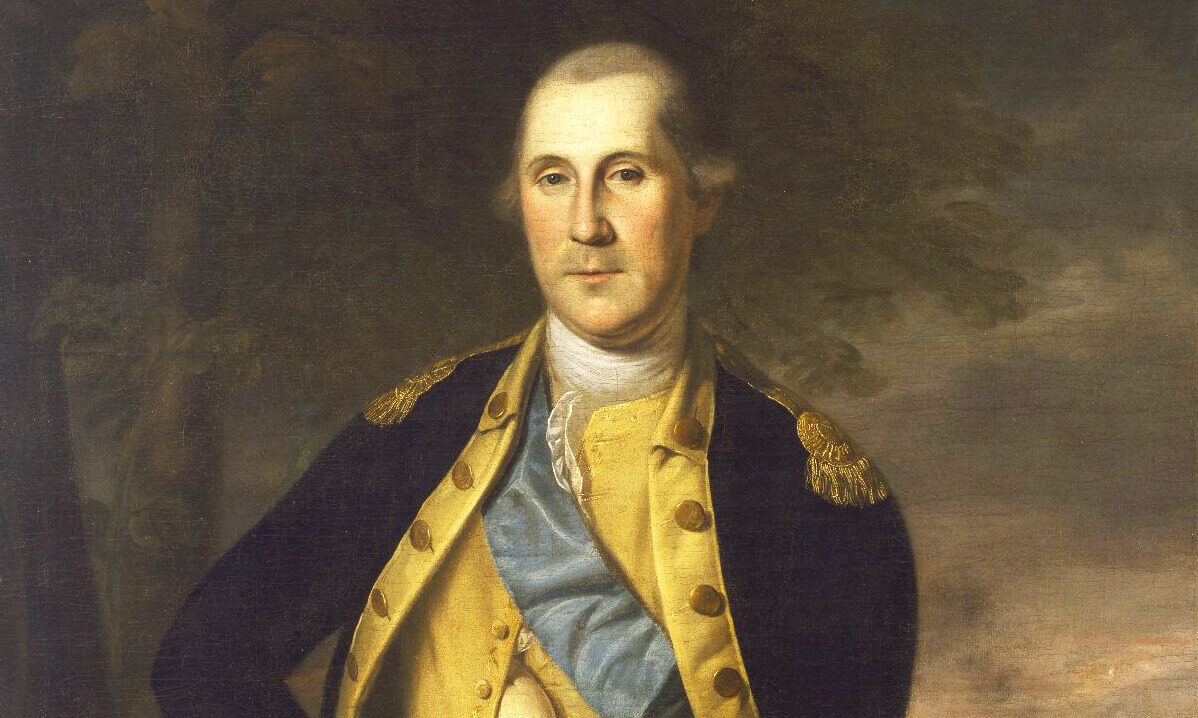
In 1775 (a year before our official separation from Great Britain), Commander-in-Chief George Washington addressed Continental soldiers and from the beginning charged them:
While we are contending for our own liberty, we should be very cautious of violating the rights of conscience in others, ever considering that God alone is the judge of the hearts of men and to Him only in this case they are answerable.14
With America’s official break from Great Britain in 1776, the states created their very first state constitutions and specifically secured the religious toleration, non-coercion, and the rights of conscience. For example, the 1776 constitution of Virginia declared:
[R]eligion . . . can be directed only by reason and conviction, not by force and violence; and therefore all men are equally entitled to the free exercise of religion according to the dictates of conscience.15
The 1776 Constitution of New Jersey similarly protected the rights of conscience,16 causing Governor William Livingston (a signer of the U. S. Constitution) to happily proclaim:
Consciences of men are not the objects of human legislation. . . . In contrast with this spiritual tyranny, how beautiful appears our catholic [expansive] constitution in disclaiming all jurisdiction over the souls of men, and securing (by a never-to-be-repealed section) the voluntary, unchecked, moral suasion of every individual – and his own self-directed intercourse with the Father of Spirits!17
When New York’s first constitution (1777) likewise protected the rights of conscience,81 Governor John Jay (an author of the Federalist Papers and the original Chief Justice of the U. S. Supreme Court) similarly rejoiced that:
Adequate security [under our constitution] is also given to the rights of conscience and private judgment. They are by nature subject to no control but that of Deity, and in that free situation they are now left. Every man is permitted to consider, to adore, and to worship his Creator in the manner most agreeable to his conscience.19
Similar clauses securing the rights of religious conscience also appeared in many other early state constitutions, including that of Delaware (1776),20 North Carolina (1776),21 Pennsylvania (1776),22 Vermont (1777),23 South Carolina (1778),24 Massachusetts (1780),25 New Hampshire (1784),26 etc. Today, the safeguards for the rights of conscience explicitly appear in forty-five state constitutions, and by inference in the other five.27
Federal Era
In 1788 following the ratification of the federal Constitution, six states submitted proposals for a Bill of Rights,28 with several specifically recommending national language that “all men have an equal, natural, and unalienable right to the free exercise of religion, according to the dictates of conscience.”29 Although the word “conscience” did not ultimately appear in the final language of the religion clauses of the First Amendment, those who framed that Amendment believed that by preventing the government from establishing a national religion and by guaranteeing to the people their “free exercise of religion,” that the rights of conscience had been fully secured30 – a fact affirmed by President Thomas Jefferson when he penned his famous letter to the Danbury Baptists assuring them that the First Amendment was an “expression of the supreme will of the nation in behalf of the rights of conscience.”31 Subsequent constitutional commentaries reiterated that the First Amendment did indeed protect the rights of conscience.32
Founding Fathers
In addition to the several Founders already mentioned, here are a few more unequivocal declarations regarding the constitutional duty of official to protect and defend the rights of religious conscience:
Government is instituted to protect property of every sort. . . . Conscience is the most sacred of all property.33 JAMES MADISON
No provision in our Constitution ought to be dearer to man than that which protects the rights of conscience against the enterprises of the civil authority.34 It behooves every man who values liberty of conscience for himself to resist invasions of it in the case of others, or their case may, by change of circumstances, become his own.35 Our rulers can have no authority over such natural rights only as we have submitted to them. The rights of conscience we never submitted – we could not submit. We are answerable for them to our God.36 THOMAS JEFFERSON
[T]he consciences of men are not the objects of human legislation. . . . For what business, in the name of common sense, has the magistrate (distinctly and singly appointed for our political and temporal happiness) with our religion, which is to secure our happiness spiritual and eternal? . . . [T]he state [does not] have any concern in the matter. For in what manner doth it affect society . . . in what outward form we think it best to pay our adoration to God?37 WILLIAM LIVINGSTON, SIGNER OF THE CONSTITUTION
Modern Era
As a result of the conscience protections long provided in American history and law, government exemptions are routinely granted to those whose religious faith requires them to participate in, or refrain from activities that violate their religious conscience. For example:
- Pacifists and conscientious objectors are not forced to fight in wars;38
- Jehovah’s Witnesses are not required to say the Pledge of Allegiance in public schools;39
- The Amish are not required to complete the standard compulsory twelve years of education;40
- Christian Scientists are not forced to have their children vaccinated or undergo medical procedures often required by state laws;41
- Muslim and Jewish men are not required to shave their beards in jobs that otherwise require employees to be clean-shaven;42
- Seventh-Day Adventists cannot be penalized for refusing to work at their jobs on Saturday;43
and there are additional examples.
Conclusion
Clearly, protection for the inalienable rights of religious conscience is deeply embedded into the fabric of American governmental policy. But as currently demonstrated in countless nations around the world, and now in America, when secularism or any other non-Biblical philosophy becomes dominant in its culture, a loss of legal protections for religious rights is usually one of the first casualties of the change.
Today in America, to seek to provide protection for the traditional rights of religious conscience is now regularly denounced as discriminatory.44 The LGBT movement, and those in government aligned with it, disdain the rights of religious conscience and instead use the power, penalties, and full force of the law to coerce all others to embrace and participate in affirming their views, including Christian bakers,45 florists,46 photographers,47 churches,48 homeowners,49 pastors,50 clerks,51 business owners,52 officials,53 religious schools,54 military personnel,55 sportscasters,56 and others.57
Our Framers recognized that if religious liberties and our civil liberties were inseparable – that if our religious liberties were diminished, our civil liberties would soon follow. As Joseph Story (a “Father of American Jurisprudence,” placed on the Supreme Court by President James Madison) pointed out:
There is not a truth to be gathered from history more certain or more momentous than this: that civil liberty cannot long be separated from religious liberty without danger, and ultimately without destruction to both. Wherever religious liberty exists, it will, first or last, bring in and establish political liberty.58
Signer of the Declaration John Witherspoon concurred:
There is not a single instance in history in which civil liberty was lost and religious liberty preserved entire. . . . God grant that in America true religion and civil liberty may be inseparable and that the unjust attempts to destroy the one may in the issue tend to the support and establishment of both.59
And Jedidiah Morse (a pastor, educator, and historian of the American Revolution, appointed by the federal government to document the condition of Indian affairs) agreed:
All efforts made to destroy the foundations of our Holy Religion ultimately tend to the subversion also of our political freedom and happiness. In proportion as the genuine effects of Christianity are diminished in any nation . . . in the same proportion will the people of that nation recede from the blessings of genuine freedom.60
Secularism produces an antipathy toward religion and religious rights, when ultimately diminish our civil rights. In fact, after President Obama announced that America no longer should be viewed as a Christian nation,61 he then announced that he was rescinding the traditional religious rights of conscience for those working in the medical profession.62 Historically, governmental protection for religious rights is the only sure indicator of protection for other non-religious civil rights.
Endnotes
1 John Quincy Adams, A Discourse on Education Delivered at Braintree, Thursday, October 24th, 1839 (Boston: Perkins & Marvin, 1840), 18.
2 Stephen Colwell, Politics for American Christians: A Word upon our Example as a Nation, our Labour, our Trade, Elections, Education, and Congressional Legislation (Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo & Co. 1852), 82, Tait’s Edinburgh Magazine, for 1844 (Edinburgh: William Tait, 1844), 752, “The Politics of the New Testament,” December 1844.
3 “Franklin D. Roosevelt, “Christmas Greeting to the Nation,” The American Presidency Project, December 24, 1940.
4 The Federal and State Constitutions, Colonial Charters and Other Organic Laws, ed. Francis Newton Thorpe (Washington: Government Printing Office, 1909), VI:3205-3207, “Plantation Agreement at Providence – August 27-September 6, 1640.”
5 William MacDonald, Select Charters and Other Documents Illustrative of American History 1606-1775 (New York: MacMillan Company, 1899), 104-106, “Maryland Toleration Act,” April 1649.
6 <a href=”https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015001567794;view=1up;seq=27″ target=”“blank”” rel=”noopener”>Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), VI:3211, “Charter of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations-1663.”
7 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:2537, “The Concession and Agreement of the Lords Proprietors of the Province of New Caesarea, or New Jersey, 1664.”
8 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:2771, “Charter of Carolina – 1665.”
9 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:2785, “The Fundamental Constitutions of Carolina – 1669.”
10 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:2549, “The Charter or Fundamental Laws of West New Jersey, Agreed Upon – 1676.”
11 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), I:558, “Charter of Delaware – 1701.”
12 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:3063, “Frame of Government of Pennsylvania, May 5, 1682.”
13 John Quincy Adams, A Discourse on Education Delivered at Braintree, Thursday, October 24th, 1839 (Boston: Perkins & Marvin, 1840), 28.
14 George Washington, The Writings of George Washington, ed. John C. Fitzpatrick (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1931), 3:492, to Benedict Arnold, September 14, 1775.
15 The American’s Guide: Comprising the Declaration of Independence; the Articles of Confederation; the Constitution of the United States, and the Constitutions of the Several States Composing the Union (Philadelphia: Hogan & Thompson, 1835), 180, 1776 Constitution: Bill of Rights, No. 16.
16 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:2597, “Constitution of New Jersey – 1776.”
17 William Livingston, The Papers of William Livingston, ed. Carl E. Prince (Trenton: New Jersey Historical Commission, 1980), 2:235, 237, article under the name “Cato,” originally published in the New Jersey Gazette on February 18, 1778.
18 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), V:2636-2637, “Constitution of New York – 1777.”
19 William Jay, The Life of John Jay (New York: J. & J. Harper, 1833), I:82, John Jay’s charge to the grand jury during the first term of the New York state Supreme Court.
20 Constitutions of the Several Independent States of America (New York: E. Oswald, 1786), 129.
21 Constitutions (1786), 185.
22 Constitutions (1786), 109.
23 Federal and State Constitutions, ed. Thorpe (1909), VI:3740.
24 Constitutions (1786), 215.
25 Constitutions (1786), 11-12.
26 Constitutions (1786), 4.
27 Forty-five state constitutions contain explicit language specifically singling out the rights of conscience. Five other states – Alaska, Hawaii, Louisiana, Montana, and South Carolina – use similar language to the U.S. Constitution (“make no law respecting an establishment of religion or prohibiting the free exercise thereof”). As is seen in the subsequent section, the Founding Fathers believed that this language provided specific protection for the rights of conscience.
28 Those states initially included Massachusetts, South Carolina, New Hampshire, Virginia, New York, and North Carolina; two years later in 1790, Rhode Island submitted its proposals. See Jonathan Elliot, The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution (Washington: 1836), I:322-333.
29 Anson Phelps Stokes, Church and State in the United States (New York: Harper & Brothers, 1950), 1:600-610. New Hampshire recommended an amendment stating that “Congress shall make no law touching religion, or to infringe the rights of conscience.”
30 The Debates and Proceedings in the Congress of the United States, ed. Joseph Gales (Washington: Gales and Seaton, 1834), I:757-796, August 15, 1789 to August 21, 1789.
31 Thomas Jefferson, The Writings of Thomas Jefferson, ed. H. A. Washington (Washington D.C.: Taylor & Maury, 1854), VIII:113, “Messrs. Nehemiah Dodge, Ephraim Robbins, and Stephen S. Nelson, A Committee of the Danbury Baptist Association, in the State of Connecticut,” January 1, 1802.
32 See, for example, Joseph Story, Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States (Boston: Hilliard, Gray, and Company, 1833), I:701, § 990-991:
The rights of conscience are, indeed, beyond the just reach of any human power. They are given by God, and cannot be encroached upon by human authority, without a criminal disobedience of the precepts of natural, as well as revealed religion. The real object of the amendment was, not to countenance, much less to advance Mahometanism, or Judaism, or infidelity, by prostrating Christianity; but to exclude all rivalry among Christian sects, and to prevent any national ecclesiastical establishment, which should give to an hierarchy the exclusive patronage of the national government. It thus sought to cut off the means of religious persecution, (the vice and pest of former ages,) and the power of subverting the rights of conscience in matters of religion, which had been trampled upon almost from the days of the Apostles to the present age.
St. George Tucker, Blackstone’s Commentaries: with Notes of Reference, to the Constitution and Laws, of the Federal Government of the United States; and of the Commonwealth of Virginia (Philadelphia: William Young Birch and Abraham Small: 1803), I:489, “Appendix: Note G. Of the Right of Conscience; and Of the Freedom of Speech and Of The Press”:
Liberty of conscience in matters of religion consists in the absolute and unrestrained exercise of our religious opinion, and duties, in that mode which our own reason and conviction dictate, without the control or intervention of any human power or authority whatsoever. This liberty though made a part of our constitution, and interwoven in the nature of man by his Creator, so far as the arts of fraud and terrors of violence have been capable of abridging it, hath been the subject of coercion by human laws in all ages and in all countries as far as the annals of mankind extend.
James Wilson, Thomas McKean [Wilson and McKean both signed the Declaration of Independence, and Wilson was a signer of the Constitution and an original Justice on the U. S. Supreme Court], Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States of America (London: 1791), II:61:
In the third place we are told, that there is no security for the rights of conscience. I ask the honorable gentleman, what part of this system puts it in the power of Congress to attack those rights? When there is no power to attack, it is idle to prepare the means of defense.
And others.
33 James Madison, The Writings of James Madison, ed. Gaillard Hunt (New York: G. P. Putnam’s Sons, 1906), VI:102, “Property,” originally published in The National Gazette on March 29, 1792.
34 Thomas Jefferson, The Writings of Thomas Jefferson, ed. H. A. Washington (New York: Biker, Thorne, & Co., 1854), VIII:147, to the Society of the Methodist Episcopal Church at New London, CT on February 4, 1809.
35 Thomas Jefferson, Memoir, Correspondence, and Miscellanies, ed. Thomas Jefferson Randolph (Charlottesville: F. Carr, an Co., 1829), III:507, to Benjamin Rush on April 21, 1803.
36 Thomas Jefferson, Notes on the State of Virginia (London: John Stockdale, 1787), 265, “Query XVII: The different religions received into that state?”
37 William Livingston, Papers, ed. Prince (1980), 2:235, 237, article under the name “Cato,” originally published in the New Jersey Gazette on February 18, 1778; Hezekiah Niles, Principles and Acts of the Revolution in America: Or, An Attempt to Collect and Preserve Some of the Speeches, Orations, & Proceedings (Baltimore: William Ogden Niles, 1822), 306-307, “Remarks on liberty of conscience, ascribed to his excellency William Livingston, governor of New Jersey, 1778”; B. F. Morris, Christian Life and Character of the Civil Institutions of the United States, Developed in the Official and Historical Annals of the Republic (Philadelphia: George W. Childs, 1864), 162-163, from William Livingston.
38 United States v. Seeger, 380 U.S. 163 (1965).
39 West Virginia State Board of Education v. Barnette, 319 U.S. 624 (1943).
40 Wisconsin v. Yoder, 406 U.S. 205 (1972).
41 See, for example, “Parents claim religion to avoid vaccines for kids,” NBCNews, October 17, 2007; “Vaccination Exemptions,” College of Physicians of Philadelphia (accessed on May 9, 2016).
42 Potter v. District of Columbia, Civil Action No. 01-1189 (D.D.C. Sept. 28, 2007).
43 Hobbie v. Unemployment Appeals Commission of Florida, 480 U.S. 136 (1987); Sherbert v. Verner, 374 U.S. 398, 409 (1963).
44 See, for example, Adam Serwer, “Arizona passes law allowing discrimination,” MSNBC, February 21, 2014; Paresh Dave, “Miss. governor signs religious freedom bill; civil rights groups dismayed,” Los Angeles Times, April 4, 2014; Chris Johnson, “Georgia Senate passes religious discrimination bill,” Washington Blade, March 5, 2015; Tony Cook, “Gov. Mike Pence signs ‘religious freedom’ bill in private,” IndyStar, April 2, 2015; Monica Davey, “Indiana and Arkansas Revise Rights Bills, Seeking to Remove Divisive Parts,” The New York Times, April 2, 2015; Timothy Holbrook, “Georgia, North Carolina bills are about LGBT discrimination. Period,” CNN, March 28, 2016; Marina Fang, “Tennessee Legislature Resurrects Discriminatory Transgender Bathroom Bill,” Huffington Post, April 6, 2016.
45 See, for example, Ken Klukowski, “Baker Faces Prison for Refusing to Bake Same-Sex Wedding Cake,” Breitbart, December 12, 2013; Chris Enloe, “‘Sweet Cakes’ Owners’ Bank Accounts Seized as Damages for Refusing to Bake Wedding Cake for Lesbian Couple,” The Blaze, December 29, 2015.
46 See, for example, Danny Burk, “A florist loses religious freedom, and much more,” CNN, February 20, 2015.
47 See, for example, Ken Klukowski, “New Mexico Court: Christian Photographer Cannot Refuse Gay-Marriage Ceremony,” Breitbart, August 22, 2013; Kristine Marsh, “Gays Force San Francisco Wedding Photographers to Close Shop,” MRC NewsBusters, November 21, 2014; Samuel Smith, “Christian Videographer Faces Legal Action After Refusing to Work Lesbian Wedding, Says It’s Against Her Biblical Beliefs,” Christian Post, March 18, 2015.
48 See, for example, Molly Montag, “Group asks IRS to investigate Cornerstone Church,” Sioux City Journal, October 1, 2010; “Southern Baptists draw distance from harsh anti-gay rhetoric, yet hold to convictions,” Baptist Press, May 24, 2012.
49 See, for example, Andrea Peyser, “Couple fined for refusing to host same-sex wedding on their farm,” New York Post, November 10, 2014.
50 See, for example, Todd Starnes, “Fired for preaching: Georgia dumps doctor over church sermons,” Fox News, April 20, 2016; Natalie Jennings, “Louie Giglio pulls out of inauguration over anti-gay comments,” The Washington Post, January 10, 2013.
51 See, for example, Allan Smith, “Anti-gay-marriage Kentucky clerk jailed for refusing to issue same-sex marriage licenses,” Business Insider, September 3, 2015; Jim Douglas, “Hood County is focal point of same-sex debate,” WFAA, July 1, 2015.
52 See, for example, Katie Zezima, “Couple Sues a Vermont Inn for Rejecting Gay Wedding,” The New York Times, July 19, 2011; Billy Hallowell, “Lesbian Couple Wins Discrimination Lawsuit Against Religious Bed and Breakfast Owner Who Denied Them a Room,” The Blaze, April 16, 2013; Justin Moyer, “Kentucky T-shirt printer that wouldn’t make gay pride shirts vindicated by court,” The Washington Post, April 28, 2015; Charlie Butts, “Iowa couple fined for refusing gay wedding: ‘We are still here’,” OneNewsNow, June 3, 2015.
53 See, for example, Kathleen Gilbert, “San Diego firefighters victorious in suit against forced participation in gay pride parade,” Life Site News, January 28, 2011; Eryn Sun, “Court Affirms CDC’s Firing of Counselor Over Same-Sex Advice,” Christian Post, February 8, 2012; Ryan T. Anderson, “Atlanta Fire Chief Fired for Expressing Christian Beliefs,” The Daily Signal, January 8, 2015; “Utah officer who objected to role in gay pride parade says he was unfairly labeled a bigot,” Fox News, February 25, 2015; Randy Ludlow, “Ohio judges who perform weddings must marry same-sex couples,” The Columbus Dispatch, August 11, 2015.
54 See, for example, “Evangelical College Gay Rights Stand Causes Uproar,” NewsMax, November 2, 2014; “Gay Teacher Files Sex Discrimination Claim Against Georgia School,” NPR, July 9, 2014; “Lesbian teacher who was fired for becoming pregnant sues Catholic school for discrimination,” Daily Mail, August 22, 2014.
55 See, for example, Todd Starnes, “Fox Exclusive: Airman Faces Punishment for her Religious Beliefs,” Fox News, August 6, 2013; Kirsten Anderson, “Air Force Sergeant claims he was fired for refusing to endorse gay ‘marriage’: faces court martial,” Life Site News, September 10, 2013; “Navy Threatens To End 19-Year Career Of Decorated Chaplain Who Served Navy SEAL Teams, According To Liberty Institute,” PR Newswire, March 9, 2015.
56 See, for example, Melissa Barnhart, “Fox Sports Southwest Charged With Discrimination for Firing Craig James Over Homosexuality Remarks,” Christian Post, March 7, 2014; Ahiza Garcia, “‘I’m not transphobic,’ says ex-ESPN analyst Curt Schilling,” CNN Money, April 22, 2016.
57 See, for example, “Missouri school sued by student who refused to support gay adoptions,” USA Today, November 2, 2006; Paul Strand, “University Employee Punished over Marriage Petition,” CBN News, October 18, 2012; Billy Hallowell, “Christian Product Engineer Claims Ford Motor Fired Him for Voicing His Bible-Based Opposition to the Company’s Promotion of ‘Pro-Homosexual Ideas’ — Now He’s Fighting Back,” The Blaze, January 28, 2015.
58 Joseph Story, A Discourse Pronounced at the Request of the Essex Historical Society, on the 18th of September, 1828, in Commemoration of the First Settlement of Salem, in the State of Massachusetts (Boston: Hilliard, Gray, Little, and Wilkins, 1828), 46.
59 John Witherspoon, The Dominion of Providence over the Passions of Men. A Sermon, Preached at Princeton, on the 17th of May, 1776. Being the General Fast appointed by the Congress through the United Colonies (Philadelphia: 1777), 27-28, 38.
60 Jedidiah Morse, A Sermon, Exhibiting the Present Dangers and Consequent Duties of the Citizens of the United States of America. Delivered at Charlestown. April 25, 1799, The Day of the National Fast (MA: Printed by Samuel Etheridge, 1799), 9.
61 Aaron Klein, “Obama: America is ‘no longer Christian’,” WorldNetDaily, June 22, 2008. See also David Brody, The Brody File, “Exclusive: Barack Obama E-mails the Brody File,” CBN News, July 29, 2007; “Obama says U.S., Turkey can be model for world,” CNN, April 6, 2009.
62 See, for example, Rob Stein, “Obama Plans to Roll Back ‘Conscience’ Rule Protecting Health Workers Who Object to Some Types of Care,” The Washington Post, February 28, 2009; Saundra Young, “White House set to reverse health care conscience clause,” CNN, February 27, 2009; Rob Stein, “Obama administration replaces controversial ‘conscience’ regulation for health-care workers,” The Washington Post, February 18, 2011.
* This article concerns a historical issue and may not have updated information.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
More Resources
Know the Truth and Protect Your Freedoms.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
Stay Informed with the Latest Resources
Enter your email address to receive our regular newsletter, with important information and updates right in your inbox!