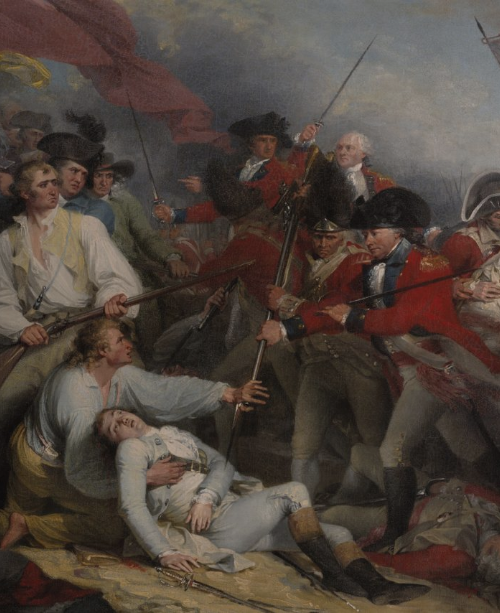
March 17 is annually celebrated in Boston as “Evacuation Day,” commemorating the departure of the British from the city1 after an extended eleven month occupation2 at the start of the American War for Independence. That occupation lasted from April 19, 1775, through March 17, 1776, encompassing the Siege of Boston3 and including early notable events of the War, such as the Battles of Lexington and Concord,4 Bunker Hill,5 and George Washington taking command of the American army.6
March 17 is annually celebrated in Boston as “Evacuation Day,” commemorating the departure of the British from the city1 after an extended eleven month occupation2 at the start of the American War for Independence. That occupation lasted from April 19, 1775, through March 17, 1776, encompassing the Siege of Boston3 and including early notable events of the War, such as the Battles of Lexington and Concord,4 Bunker Hill,5 and George Washington taking command of the American army.6
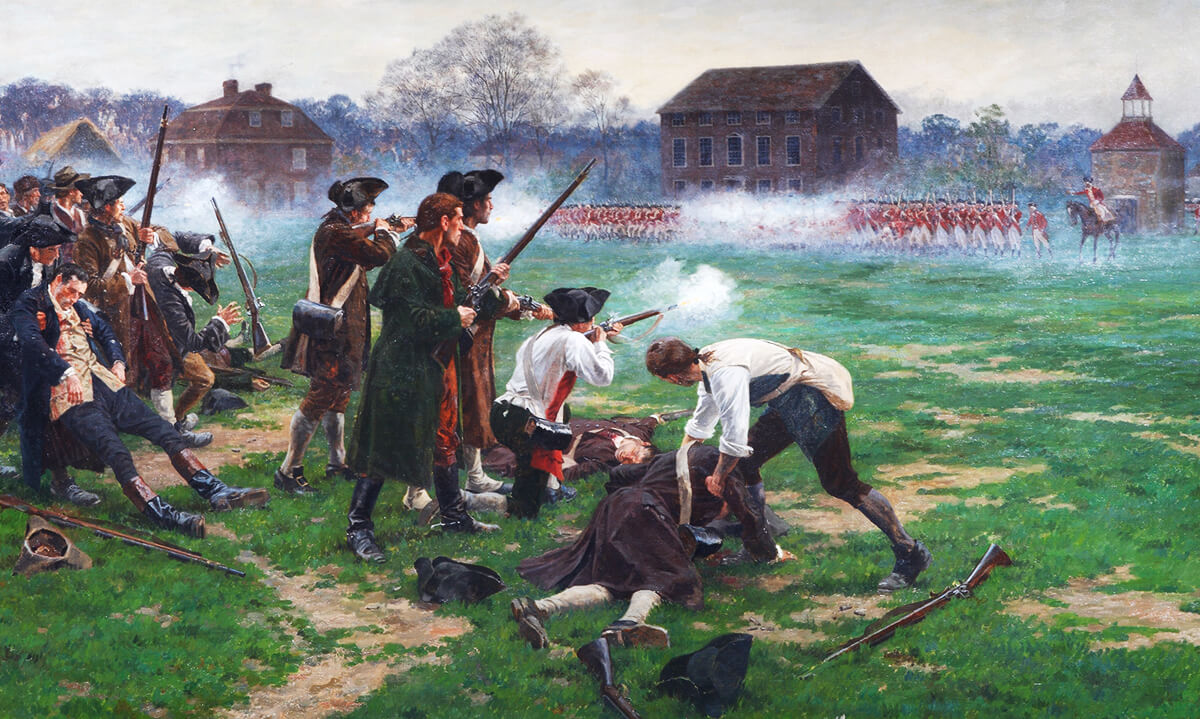
The occupation started when British leader Thomas Gage led troops into Boston, and then dispatched hundreds to seize or destroy ammunition stored in Concord.7 Riders such as Paul Revere set out to warn local inhabitants,8 and also to alert John Hancock and Samuel Adams (who were under threat of death by the British9) of the approach of the British army.
 Hancock and Adams were staying in the home of Lexington Pastor Jonas Clark.10 Pastor Clark and 77 militia from his church11 gathered to meet the approaching British–a skirmish easily won by the 800 British troops.12 (In the WallBuilders library is a sermon preached by Jonas Clark on the one-year anniversary of the Battle of Lexington.13)
Hancock and Adams were staying in the home of Lexington Pastor Jonas Clark.10 Pastor Clark and 77 militia from his church11 gathered to meet the approaching British–a skirmish easily won by the 800 British troops.12 (In the WallBuilders library is a sermon preached by Jonas Clark on the one-year anniversary of the Battle of Lexington.13)
After Lexington, the British pressed on to Concord, where they were met by Rev. William Emerson and some 400 Americans.14 After the British suffered casualties in that skirmish, they retreated to Boston,15 and all along the way, British forces were fired upon by American militias from the surrounding countryside, including those led by pastors such as Philips Payson and Benjamin Balch.16 (Many additional preachers also fought in other engagements throughout the War.17)
Evacuation Day is a reminder of the courage and backbone shown by the spiritual leaders of earlier generations–a spiritual leadership still badly needed today!
Endnotes
1 “March 17, 1901: Boston Celebrates First Evacuation Day,” Mass Moments, accessed January 17, 2024.
2 “Siege of Boston,” Massachusetts Historical Society, accessed January 17, 2024.
3 Richard Frothingham, History of the Siege of Boston, and of the Battles of Lexington and Concord, and Bunker Hill (Boston: Charles C. Little and James Brown, 1851), 91-119.
4 “Lexington and Concord,” US History, accessed January 17, 2024.
5 Frothingham, History of the Siege of Boston (1851), 121-132.
6 “Washington takes command of Continental Army in 1775,” US Army, April 15, 2016.
7 Frothingham, History of the Siege of Boston (1851), 55.
8 “The Real Story of Paul Revere’s Ride,” The Paul Revere House, accessed January 17, 2024.
9 “Attempted Capture of John Hancock and Samuel Adams,” WallBuilders.
10 J. T. Headley, The Chaplains and Clergy of the Revolution (NY: Charles Scribner, 1864), 78.
11 Jonas Clark, “Sermon-Battle of Lexington-1776,” WallBuilders.
12 Benson J. Lossing, A History of the United States for Families and Libraries (NY: Mason Brothers, 1860), 232.
13 Jonas Clark, “Sermon-Battle of Lexington-1776,” WallBuilders.
14 Benson J. Lossing, A History of the United States, From the Discovery of the American Continent (Boston: Little, Brown, and Company, 1864), VII:290, 299.
15 Lossing, History of the United States (1864), VII:303-306.
16 Headley, Chaplains and Clergy (1864), 60; Balch Leaflets (Salem, MA: Eben Putnam, 1896-1897), 28.
17 Daniel Dorchester, Christianity in the United States From the First Settlement Down to the Present Time (NY: Hunt & Eaton, 1889), 265.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
More Resources
Know the Truth and Protect Your Freedoms.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
Stay Informed with the Latest Resources
Enter your email address to receive our regular newsletter, with important information and updates right in your inbox!