Was the American Revolution an act of rebellion against God and the Bible? Many today claim that it was. For example, John McArthur (Pastor of Grace Community Church and host of the national radio program “Grace to You”) asserts:
People have mistakenly linked democracy and political freedom to Christianity. That’s why many contemporary evangelicals believe the American Revolution was completely justified, both politically and scripturally. They follow the arguments of the Declaration of Independence, which declares that life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness are Divinely endowed rights. . . . But such a position is contrary to the clear teachings and commands of Romans 13:1-7. So the United States was actually born out of a violation of New Testament principles, and any blessings God has bestowed on America have come in spite of that disobedience by the Founding Fathers.1
Oklahoma church leader Albert Soto similarly claims:
The Colonists’ act of rebellion flies in the face of [Romans 13:1,2]. Did they overlook this verse? No, these were not men ignorant of Scripture. In fact, they used Scripture to support their cause in the most devious of ways. The deception that prevailed during this period of history was immense. God and Scripture was the vehicle of mobilization that unified the cause, gave it credence, and allowed the Deist leaders at the top to move the masses toward rebellion. Scripture was the Forefathers’ most useful tool of propaganda.2
Others hold the same position.3 In fact, Dr. Daryl Cornett of Mid-America Theological Seminary maintains that the American Revolution occurred because . . .
Deistic and Unitarian tendencies in regards to religion. . . . were of such strength that even orthodox Christians were swept up into rebellion against their governing authorities. . . . Those Christians who supported physical resistance against the tyranny of Britain generally turned to Enlightenment rhetoric for validation, propped up by poor exegesis and application of the Bible.
While such charges certainly reflect the personal views of these critics, they definitely do not accurately reflect the extended theological debates that occurred at the time of the American Revolution. In fact, contrary to Dr. Cornett’s claim that the Founding Fathers “turned to Enlightenment rhetoric for validation” of the American Revolution, the topic of civil disobedience and resistance to governing authorities had been a subject of serious theological inquiries for centuries before the Enlightenment. This was especially true during the Reformation, when the subject was directly addressed by theologians such as Frenchman John Calvin,4 German Martin Luther,5 Swiss Reformation leader Huldreich Zwingli,6 and numerous others.7
It was not strange that such Biblical discussions should have arisen in that period, for many tyrannical civil leaders who felt personally threatened by Biblical Reformation teachings attempted to suppress the spread of those teachings through bloody purges, brutal tortures, and barbaric persecutions – such as when French leaders conducted the famous St. Bartholomew’s Day Massacre in 1572, resulting in 110,000 Reformation followers being killed, or when Henry VIII (1491-1547) similarly utilized public executions and burnings at the stake (a practice continued by Edward VI, Mary, Elizabeth I, and subsequent monarchs). In fact, those civil leaders even deliberately enacted laws specifically prohibiting Reformation adherents from practicing their Scriptural beliefs.
Facing such civil opposition, Reformation leaders turned to the Bible and found much guidance on the subject of civil disobedience and resistance to tyrannical civil authority. In fact, numerous famous heroes of the Bible – including many of those listed in the “Faith Hall of Fame” in Hebrews 11 as well as in other passages – were accorded their special position of honor because they committed civil disobedience (e.g., Daniel, the Three Hebrew Children, the Hebrew midwives, Rahab, Moses, etc.; and the Apostles in Acts 4-5 also declared their willingness to be civilly disobedient against tyrannical commands of civil and religious rulers).
Some of the important theological works on the subject of civil disobedience and resistance published during that time included the 1556 Short Treatise of Politic Power and of the True Obedience which Subjects Owe to Kings and Other Civil Governors by Bishop John Poynet (1516-1566), and the 1579 Vindiciae Contra Tyrannos (A Defense Of Liberty Against Tyrants), published by French Reformation theologian Philippe Duplessis-Mornay (1549-1623) and French Reformation leader Hubert Languet (1518-1581) in response to the horrific St. Bartholomew Day Massacre. Both works undertook an in-depth Biblical examination of how God’s people throughout the Scriptures had responded to civil rulers, including both good and bad rulers. Those theological discussions continued in England during the brutal reign of Henry VIII (1491-1547), the repressive abuses of James I (1566-1625), and the ruthless rule of the Tudor monarchs, including that of Bloody Mary (1516-1558).
In fact, James I, in addition to using brutal persecutions and murders to help combat the theological teachings and writings leveled against him, even ordered Church leaders (recall that James I was the official head of the English Church) to concoct two new “church” doctrines: (1) the Divine Right of Kings (that kings stand in the place of God, representing Him to the people), and (2) Complete Submission and Non-Resistance to Authority (that because kings have an allegedly Divine position, they are not to be resisted – ever, for any reason). Not surprisingly, Reformation followers openly opposed James’ “irrational and unscriptural doctrines,”8 thus prompting him to level even harsher persecutions against them, including mutilation, hanging, and disemboweling.
In 1644, at a time of unlimited monarchies wherein the king was the absolute law, Scottish theologian Samuel Rutherford penned the important theological work Lex Rex, demonstrating that the law is king rather than vice versa. For asserting that Biblical position, Rutherford was eventually charged by British monarchy with high treason but died before he could be tried. Not surprisingly, Lex Rex was banned by the Crown and every person who had a copy was ordered to turn it in to a king’s official.
James II continued the persecution of believers, and not surprisingly, the theological debates also continued. For example, when clergyman Abednego Seller penned a defense of James’ reign, urging complete obedience to the Crown in his Passive Obedience Prov’d to be the Doctrine of the Church of England, from the Reformation to These Times (London, 1689), clergyman Samuel Johnson responded with An Answer to the History of Passive Obedience (London, 1689).
Significantly, the many theological writings penned during these brutal and tyrannical reigns provided the underpinning for the Glorious Revolution of 1688 in which: (1) tyrannical monarchs were set aside; (2) England made its first attempts to separate State from Church and thus end religious tyranny and murders wrongly committed in the name of Christ; and (3) representative government was instituted under William of Orange (1650-1702).
When British autocratic tyranny began to increase toward America preceding the Revolution, those ancient theological debates were renewed. The Quakers and Anglicans adopted the position set forth by King James I (and subsequently embraced by Dr. Cornett, Rev. MacArthur, and others of today’s critics), but the Presbyterians, Lutherans, Baptists, Congregationalists, and most other denominations of that day adopted the theological viewpoint presented by Luther, Calvin, Zwingli, Rutherford, Poynet, Mornay, Languet, Johnson, and other theologians across the centuries. In fact, John Adams specifically recommended the theological works of Poynet (A Short Treatise of Politic Power, 1556) and Duplessis-Mornay and (A Defense Of Liberty Against Tyrants, 1579) to readers who wanted to understand the theological thinking in the American founding.9
On the basis of those numerous historic theological writings (which, significantly, had also been regularly preached from American pulpits for decades prior to the American Revolution10), Americans embraced two specific theological positions that guided their thinking and conduct in the conflict with Great Britain.
The first was that most Christian denominations during the Founding Era held that while they were forbidden to overthrow the institution of government and live in anarchy, they were not required blindly to submit to every law and policy. Those in the Founding Era understood that the general institution of government was unequivocally ordained by God and was not to be overthrown, but that did not mean that God approved every specific government; God had ordained government in lieu of anarchy – He opposed anarchy, rebellion, lawlessness, and wickedness and wanted civil government in society. Therefore, a crucial determination in the colonists’ Biblical exegesis was whether opposition to authority was simply to resist the general institution of government (an institution ordained by God Himself), or whether it was instead to resist tyrannical leaders who had themselves rebelled against God. (The Scriptural model for this position was repeatedly validated when God Himself raised up leaders such as Gideon, Ehud, Jepthah, Samson, and Deborah to throw off tyrannical governments – leaders subsequently praised in Hebrews 11:32 for those acts of faith.) That the Founders held the view that the institution of government is not to be opposed but that tyranny is, is a position clearly evident in their writings.
For example, Founding Father James Otis explained that the only king who had a “Divine right” was God Himself; beyond that, God had ordained that power should rest with the people (c.f., Exodus 18:21, Deuteronomy 1:15-16, etc.):
Has it [government] any solid foundation? – any chief cornerstone. . . ? I think it has an everlasting foundation in the unchangeable will of God. . . . Government. . . . is by no means an arbitrary thing depending merely on compact or human will for its existence. . . . There can be no prescription old enough to supersede the law of nature and the grant of God Almighty, Who has given to all men a natural right to be free; and they have it ordinarily in their power to make themselves so if they please….If both those powers are retained in the hands of the many (where nature seems to have placed them originally), the government is a simple democracy, or a government of all over all. . . . [God is] the only monarch in the universe Who has a clear and indisputable right to absolute power because He is the only one Who is omniscient as well as omnipotent.11
Founding Father John Dickinson (a signer of the Constitution) also affirmed that spiritual view:
Kings or parliaments could not give the rights essential to happiness. . . . We claim them from a higher source – from the King of kings and Lord of all the earth. They are not annexed to us by parchments and seals. They are created in us by the decrees of Providence, which establish the laws of our nature. They are born with us, exist with us, and cannot be taken from us by any human power without taking our lives.12
In fact, Samuel Adams (the “Father of the American Revolution” and a signer of the Declaration of Independence) specifically recommended a study of the Scriptures in order to understand the basis of America’s struggle against a tyrannical king, explaining that:
The Rights of the Colonists as Christians. . . . may be best understood by reading and carefully studying the institutes of the great Law Giver and Head of the Christian Church, which are to be found clearly written and promulgated in the New Testament.13
The Founders clearly believed that they were not in rebellion to God’s ordained institution of civil government; they were only resisting tyranny and not the institution itself. In fact, Rev. Jacob Duché (a supporter of the British) argued from the Bible in favor of the American position, explaining:
Inasmuch as all rulers are in fact the servants of the public and appointed for no other purpose than to be “a terror to evil-doers and a praise to them that do well” [c.f., Rom. 13:3], whenever this Divine order is inverted – whenever these rulers abuse their sacred trust by unrighteous attempts to injure, oppress, and enslave those very persons from whom alone, under God, their power is derived – does not humanity, does not reason, does not Scripture, call upon the man, the citizen, the Christian of such a community to “stand fast in that liberty wherewith Christ….hath made them free!” [Galatians 5:1] The Apostle enjoins us to “submit to every ordinance of man for the Lord’s sake,” but surely a submission to the unrighteous ordinances of unrighteous men, cannot be “for the Lord’s sake,” for “He loveth righteousness and His countenance beholds the things that are just.”14
Despite the Americans embracing what they believed to be a fully-supported Biblical position, some British leaders nevertheless specifically accused the Americans of anarchy and rebellion – a charge to which John Quincy Adams forcefully responded:
[T]here was no anarchy. . . . [T]he people of the North American union and of its constituent states were associated bodies of civilized men and Christians in a state of nature but not of anarchy. They were bound by the laws of God (which they all) and by the laws of the Gospel (which they nearly all) acknowledged as the rules of their conduct.15 (emphasis added)
Declaration signer Francis Hopkinson (also a church musician and choir leader) agreed:
Q. It has often been said, that America is in a state of rebellion. Tell me, therefore, what is Rebellion?
A. It is when a great number of people, headed by one or more factious leaders, aim at deposing their lawful prince without any just cause of complaint in order to place another on his throne.Q. Is this the case of the Americans?
A. Far otherwise.16
Reflective of the Founding Father’s belief that they were not rebelling against God or resisting ordained government but only tyranny was the fact that the first national motto proposed for America in August 1776 was “Rebellion to tyrants is obedience to God”17 – a summation of the famous 1750 sermon18 preached by the Rev. Dr. Jonathan Mayhew (a principle figure in the Great Awakening).
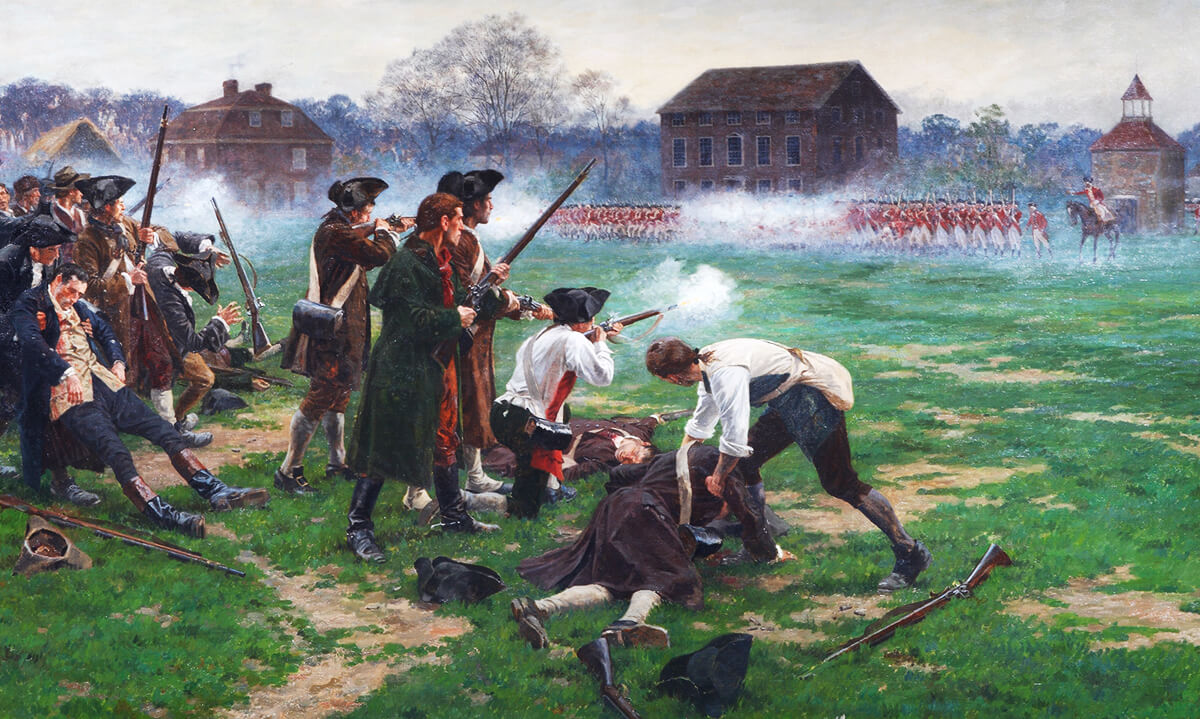
The second Scriptural viewpoint overwhelmingly embraced by most Americans during the Revolutionary Era was that God would not honor an offensive war, but that He did permit civil self-defense (e.g., Nehemiah 4:13-14 & 20-21, Zechariah 9:8, 2 Samuel 10:12, etc.). The fact that the American Revolution was an act of self-defense and was not an offensive war undertaken by the Americans remained a point of frequent spiritual appeal for the Founding Fathers. After all, Great Britain had attacked America, not vice versa; the Americans had never fired the first shot – not in the Boston Massacre of 1770, the bombing of Boston and burning of Charlestown in 1774, or in the attacks on Williamsburg, Concord, or Lexington in 1775.
Illustrative of this belief was the famous command to the Lexington Minutemen, “Don’t fire unless fired upon!” Yet, having been fired upon without having broken any law, the Americans believed they had a Biblical right to self-defense. In fact, the Rev. Peter Powers, in a famous sermon he preached in front of the Vermont Legislature in 1778,19 specifically noted that America had “taken up arms in its own defense”20 – that she had no initiated the conflict but was only defending herself after being attacked.
The Framers’ writings repeatedly emphasized this point of spiritual appeal. For example, Founding Father Francis Hopkinson made this clear in his 1777 work “A Political Catechism”:
Q. What is war?
A. The curse of mankind; the mother of famine and pestilence; the source of complicated miseries; and the undistinguishing destroyer of the human species.Q. How is war divided?
A. Into offensive and defensive.Q. What is the general object of an offensive war? . . .
A. [F]or the most part, it is undertaken to gratify the ambition of a prince, who wishes to subject to his arbitrary will a people whom God created free, and to gain an uncontrolled dominion over their rights and property. . . .Q. What is defensive war?
A. It is to take up arms in opposition to the invasions of usurped power and bravely suffer present hardships and encounter present dangers, to secure the rights of humanity and the blessings of freedom to generations yet unborn.Q. Is even defensive war justifiable in a religious view?
A. The foundation of war is laid in the wickedness of mankind . . . . God has given man wit to contrive, power to execute, and freedom of will to direct his conduct. It cannot be but that some, from a depravity of will, will abuse these privileges and exert these powers to the injury of others; and the oppressed would have no safety nor redress but by exerting the same powers in their defense and it is our duty to set a proper value upon and defend to the utmost our just rights and the blessings of life, otherwise a few miscreants [unprincipled individuals] would tyrannize over the rest of mankind, and make the passive multitude the slaves of their power. Thus it is that defensive is not only justifiable but an indispensable duty.Q. Is it upon these principles that the people of America are resisting the arms of Great Britain, and opposing force with force?
A. Strictly so. . . . And may Heaven prosper their virtuous undertaking!21
Founding Father James Wilson (a signer of both the Declaration and the Constitution, and an original Justice on the U. S. Supreme Court) affirmed:
The defense of one’s self . . . is not, nor can it be, abrogated by any regulation of municipal law. This principle of defense is not confined merely to the person; it extends to the liberty and the property of a man. It is not confined merely to his own person; it extends to the persons of all those to whom he bears a peculiar relation – of his wife, of his parent, of his child. . . . As a man is justified in defending, so he is justified in retaking his property. . . . Man does not exist for the sake of government, but government is instituted for the sake of man.22
According to the Founders’ Biblical understanding, the fact that they were engaged in a defensive action made all the difference – they believed that they could boldly approach God and sincerely seek His aid and blessing in such a situation. In fact, so cognizant were American leaders they that they would account to God for their actions – and so convinced were they that they would be held innocent before Him – that the flag of the Massachusetts Army proclaimed “An Appeal to God,” and the flag of the Massachusetts Navy likewise declared an “Appeal to Heaven.”23
The Continental Congress also issued a manifesto reflecting a similar tone of submission to God:
We, therefore, the Congress of the United States of America, do solemnly declare and proclaim that. . . . [w]e appeal to the God Who searcheth the hearts of men for the rectitude of our intentions; and in His holy presence declare that, as we are not moved by any light or hasty suggestions of anger or revenge, so through every possible change of fortune we will adhere to this our determination.24
Believing that they were thus operating under fundamental Biblical principles, Founding Father Samuel Adams therefore boldly warned British officials:
There is One above us Who will take exemplary vengeance for every insult upon His majesty. You know that the cause of America is just. You know that she contends for that freedom to which all men are entitled – that she contends against oppression, rapine, and more than savage barbarity. The blood of the innocent is upon your hands, and all the waters of the ocean will not wash it away. We again make our solemn appeal to the God of heaven to decide between you and us. And we pray that, in the doubtful scale of battle, we may be successful as we have justice on our side, and that the merciful Savior of the world may forgive our oppressors.25
Significantly, the Americans had been militarily attacked for well over two years before they finally announced a separation; and for eleven years preceding that announcement (from 1765 to 1776), they had diligently pursued reconciliation and not conflict, offering documents such as their famous appeal of 1775 and the May 1776 “Olive Branch Petition,” each of which was submitted in a completely submissive and conciliatory tone. Reflective of this tone was the writing of Founding Father Stephen Hopkins (a signer of the Declaration and Governor of Rhode Island) in which he explained to the British:
We finally beg leave to assert that the first planters of these colonies were pious Christians – were faithful [British] subjects who, with a fortitude and perseverance little known and less considered, settled these wild countries by God’s goodness and their own amazing labors [and] thereby added a most valuable dependence to the crown of Great-Britain; were ever dutifully subservient to her interests; so taught their children that not one has been disaffected to this day but all have honestly obeyed every royal command and cheerfully submitted to every constitutional law; . . . have carefully avoided every offensive measure . . . have never been troublesome or expensive to the mother country; have kept due order and supported a regular government; have maintained peace and practiced Christianity; and in all conditions and in every relation have demeaned themselves as loyal, as dutiful, and as faithful subjects ought; and that no kingdom or state hath, or ever had, colonies more quiet, more obedient, or more profitable than these have ever been.26
The Rev. Dr. John Witherspoon (also a signer of the Declaration) also affirmed:
On the part of America, there was not the most distant thought of subverting the government or of hurting the interest of the people of Great Britain, but of defending their own privileges from unjust encroachment; there was not the least desire of withdrawing their allegiance from the common sovereign [King George III] till it became absolutely necessary – and indeed, it was his own choice.27
Significantly, as Dr. Witherspoon had correctly noted, it was Great Britain who had terminated the entreaties; in fact, during the last two years of America’s appeals, her peaceful pleas were directly met by armed military force. King George III dispatched 25,000 British troops to invade his own Colonies, enter the homes of his own citizens to take their private possessions and goods, and imprison them without trials – all in violation of his own British Common Law, English Bill of Rights, and Magna Carta (centuries old documents that formed the basis of the covenant between British rulers and citizens). Only when those governmental covenants had been broken by their rulers and America had been directly attacked did the Americans respond in self-defense.
On the basis of these two theological understandings (that God Himself had ordained the institution of civil government, and that God had explicitly authorized civil self-defense) the Founding Fathers and the majority of American Christians in that day believed that they were conducting themselves in a manner that was not in rebellion to God or the Scriptures.
Consequently, Dr. Cornett’s claim, as well as those of John MacArthur and other critics, that the Founders “generally turned to Enlightenment rhetoric for validation, propped up by poor exegesis and application of the Bible” merely reflects the side that they have taken in the historic theological debate – the same as if they had been 1776 Quakers arguing against Presbyterians, or Anglicans against Congregationalists. However, just because these modern critics may disagree with the theology of Calvin, Luther, Zwingli, Mornay, Rutherford, and other theologians does not mean that from an historical viewpoint the Americans’ approach was “propped up by poor exegesis and application of the Bible,” or that the Founders “generally turned to Enlightenment rhetoric for validation.” It simply means that today’s critics are either uninformed about the actual historical and theological writings from the Reformation through the Revolution, or that they disagree with the theological positions held by the Founding Fathers, theologians, and ministers of that era, but it does not mean that there was no Biblical basis for the American Revolution.
In fact, the spiritual nature of America’s resistance was so clear even to the British that in the British Parliament:
Sir Richard Sutton read a copy of a letter relative to the government of America from a [Crown-appointed] governor in America to the Board of Trade [in Great Britain] showing that. . . . If you ask an American, “Who is his master?” He will tell you he has none – nor any governor but Jesus Christ.28
Such spiritual declarations – confirming what was readily evident even to America’s opponents – certainly are not consistent with what critics inaccurately claim is the Unitarian, Deistic, and Secular Enlightenment rebellion basis of the American Revolution.
Endnotes
1 Dr. John MacArthur, see his declaration that “the truth of the matter is that our own nation was borne out of a violation of this biblical text.” “The Christian and Government: The Christian’s Responsibility to Government – Part 1,” January 6, 1985, Grace to You, https://www.gty.org/library/sermons-library/45-97/the-christians-responsibility-to-government-part-1.
2 Albert Soto, “The American Revolution Rebellion” A True Church
3 For example, see Dr. Jack Arnold, “Dare You Resist Your Government? Romans 13: 2-4,”IIIM [Third Millennium] Magazine Online, April 16-April 22, 2001, Vol. 3, No. 16, http://cleartheology.com/expo/45Romans/NT.Arnold.Rom.59.html; Dr. John Brug, “The Christian’s Dual Citizenship: Concerning the American Revolution”; Pastor Robert L. Deffinbaugh, “Was the American Revolution Biblically Supported?” August 8, 2008, https://www.bible.org/page.php?page_id=6084; etc.
4 John Calvin, Institutes of the Christian Religion, trans. Henry Beveridge (Edinburgh: Calvin Translation Society, 1845, the first English translation by Thomas Norton was published in London: 1561, the original Latin version was published in 1536), 4:Ch. 20, https://www.ccel.org/ccel/calvin/institutes.vi.xxi.html.
5 Martin Luther, Temporal Authority: To What Extent Should it be Obeyed? (1523), https://www.uoregon.edu/~sshoemak/323/texts/luther~1.htm.
6 Americanized Encyclopedia Britannica (Chicago: Belford-Clarke Co., 1890), 6456-6457, s.v. “Huldreich Zwingli.”
7 John Harty, The Catholic Encyclopedia. (New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912), “Tyrannicide,” https://www.newadvent.org/cathen/15108a.htm; Rev. John C. Rager, “Catholic Sources and the Declaration of Independence,” The Catholic Mind, Vol. XXVIII, No. 13, July 8, 1930, https://www.catholiceducation.org/en/controversy/common-misconceptions/catholic-sources-and-the-declaration-of-independence.html.
8 J. M. Mathews, The Bible and Civil Government, in a Course of Lectures (New York: Robert Carter & Brothers, 1851), 231.
9 John Adams, A Defense of the Constitutions of Government of the United States of America (Philadelphia: William Young, 1797), III:210-211.
10 See, for example, numerous sermons cited in Alice M. Baldwin, The New England Clergy and the American Revolution (New York: Frederick Ungar, 1958), 22-23, 26, 27-28, 34-37, 65-68, 86-87, 89-95,101-104; sermons by Jonathan Mayhew, A Discourse Concerning the Unlimited Submission and Non-Resistance to the Higher Powers (Boston: 1750), 37-41, Jonathan Ellis, The Justice of the Present War against the French in America, and the Principles that Should Influence us in the Undertaking Asserted: A Sermon Preached to the Soldiers, Sept 22, A.D. 1755. from I Sam. Xviii. 17 (Newport: J. Franklin, 1755), John A. Lidenius, The Lawfulness of Defensive War. A Sermon Preached before the Members of the Church; at Chiechester, in the County of Chester, and Province of Pennsylvania, upon their Association for Defense, February 14, 1756 (Philadelphia: James Chattin, 1756), etc.
11 James Otis, The Rights of the British Colonies Asserted and Proved (Boston: J. Williams 1766), 11, 13, 16-18,
12 John Dickinson, The Political Writings of John Dickinson (Wilmington: Bonsal and Niles, 1801), I:111.
13 Samuel Adams, The Life and Public Services of Samuel Adams, ed. William V. Wells (Boston: Little, Brown, and Company, 1865), I:504.
14 Jacob Duche, The Duty of Standing Fast in our Spiritual and Temporal Liberties, A Sermon Preached in Christ Church, July 7, 1775. Before the First Battalion of the City and Liberties of Philadelphia (Philadelphia: James Humphreys, Jr., 1775), 13-14.
15 John Quincy Adams, An Address Delivered at the Request of the Committee of Arrangements for the Celebrating the Anniversary of Independence at the City of Washington on the Fourth of July 1821 upon the Occasion of Reading The Declaration of Independence (Cambridge: Hilliard and Metcalf, 1821), 28.
16 Francis Hopkinson, The Miscellaneous Essays and Occasional Writings of Francis Hopkinson, Esq. (Philadelphia: T. Dobson, 1792), I:115-116.
17 John Adams, Letters of John Adams, Addressed to His Wife, ed. Charles Francis Adams (Boston: Charles C. Little and James Brown, 1841), I:152, letter to Abigail Adams, August 14, 1776.
18 Jonathan Mayhew, A Discourse Concerning the Unlimited Submission and Non-Resistance to the Higher Powers (New York: Arno Press & The New York Times, 1968, originally printed in Boston: 1750), 37-41.
19 The Rev. Peter Powers, Jesus Christ the true King and Head of Government; A Sermon Preached before the General Assembly of the State of Vermont, on the Day of Their First Election, March 12, 1778 at Windsor (Newbury-Port: Printed by John Michael, 1778).
20 The Rev. Peter Powers, Jesus Christ the true King and Head of Government…..March 12, 1778, 18.
21 Francis Hopkinson, Miscellaneous Essays and Occasional Writings (1792), I:111-115.
22 James Wilson, The Works of the Honorable James Wilson, ed. Bird Wilson (Philadelphia: Bronson and Chuncey, 1804), II:496-497.
23 Journals of the House of Representatives of Massachusetts. 1776 (Watertown, MA: 1776), 51:III:196-197, April 29, 1776.
24 Samuel Adams, The Writings of Samuel Adams, ed. Harry Alonzo Cushing (New York: G. P. Putnam’s Sons, 1904), IV:86, “Manifesto of the Continental Congress,” October 30, 1778.
25 Samuel Adams, Writings, ed. Cushing (1904), IV:38, to the Earl of Carlisle and Others, July 16, 1778.
26 Stephen Hopkins, The Grievances of the American Colonies Candidly Examined (London: J. Almon, 1766), 45-48.
27 John Witherspoon, The Works of John Witherspoon (Edinburgh: J. Ogle, 1815), IX:250, “The Druid,” Number III.
28 Hezekiah Niles, Principles and Acts of the Revolution in America (Baltimore: William Ogden Niles, 1822), 198.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
More Resources
Know the Truth and Protect Your Freedoms.
Still looking for answers? Visit our FAQ page
Stay Informed with the Latest Resources
Enter your email address to receive our regular newsletter, with important information and updates right in your inbox!